AddressData_CrossCheck
NG911 Data Prep and AGRC’s Address Cross Check Project
Project Background
As the State of Utah moves closer to Next-Generation-911 (NG911) implementation, data prep and data clean up are the next, most logical steps for GIS readiness.
Please visit Utah's NG911 GIS Roadmap for more information on how this project fits into the larger picture. Specific to this project, the section titled Address Component Cross Check will give you a good background on why we are doing this.
Please contact Greg Bunce at AGRC to have your jurisdiction processed. In return you will receive a discrepancy report (FileGeodatabase and ArcMap document) indicating records that need further inspection.
The Address Cross Check Project
AGRC’s Address Cross Check project is guided by NG911 GIS standards established by National Emergency Number Association (NENA). To assist in complying with these standards, AGRC has created a custom process to perform validation checks on the Site/Structure Address Points and Road Centerline datasets.
The process cross-checks the address components from Site/Structure Address Points and Road Centerlines - checking for attribute, distance, and address range issues (mismatches). The project outputs a file geodatabase containing the address points and road centerlines containing possible issues, as well the input, source data for map reference. An overview of the code operations are as follows:
- Iterate through each Site/Structure Address Point and spatially searches for the two closest, matching Road Centerline segments with the same name, that are within a user-specified distance.
- The code then checks the road segments for other matching attributes including: pre direction, post type, post direction, and if the house number is contained within the segment’s address range.
- The code will also flag address points that do not find a corresponding road segment.
- Additionally, the process allows the user to define a distance in which the address point will be flagged if it falls outside of this distance range. The project can be run at any time, and AGRC will provide each jurisdiction (county/city) with the following outputs: a file geodatabase containing the output data and an ArcMap document, symbolized, so that the end-user can easily explore the data.
Notes on the Output FileGeodatabase and ArcMap document
- AddrPnts_SGID and Roads_SGID represent a snapshot of the input data, based on when the project was run.
- AddrPoints_ToCheck and Roads_ToCheck contain the records that flagged based on one of the validation checks.
- The user can view each validation check individually by way of definition queries on the following, boolean fields:

- PREDIR_ISS (indicating pre direction mismatch)
- POSTTYPE_ISS (indicating post type mismatch)
- POSTDIR_ISS (indicating post direction mismatch)
- ADDR_RANGE_ISS (indicating address range mismatch)
- NOT_FOUND (indicating the address point did not find a matching road segment)
- DIST_ISS (indicating the nearest road segment was beyond the user-defined distance radius)
- The corresponding feature can be found by using the following fields: ADDR_UID and ROAD_UID. In other words, if you’re looking at the AddrPoints_ToCheck data, you can use the ROAD_UID field to determine what road segment the validation was run on (and visa vera is you’re looking at Roads_ToCheck data).
- If you’re using the provided ‘AddressXCheck_Display.mxd’ to browse the data, a ‘relate’ has already been done using the above-mentioned fields. To select the corresponding feature, use the ‘Related Tables” option in the attribute table.
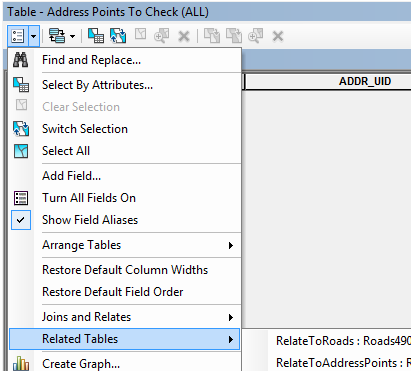
- If you’re using the provided ‘AddressXCheck_Display.mxd’ to browse the data, a ‘relate’ has already been done using the above-mentioned fields. To select the corresponding feature, use the ‘Related Tables” option in the attribute table.
- The table named, ‘tbl_Report’ can be ignored. It is used in the creation of the ‘xxxx_ToCheck’ feature classes and contains all the records that were flagged during processing.
The code for this project can be found in this GitHub Repository.